Thermal cameras, also known as infrared cameras, detect heat emitted by objects and display this as visible images. They’re valuable in various fields for their ability to “see” in total darkness and through obscurants like smoke or fog, as they pick up temperature variations rather than relying on visible light. Here’s how they work and some common applications.
How Thermal Cameras Work
Thermal cameras use infrared sensors to capture heat or infrared radiation from objects. Each pixel in a thermal camera represents a specific temperature value, which is displayed in shades of color. Cooler areas typically appear in dark colors (like blue or purple), while hotter areas show up in warm colors (like red, yellow, or white).

Applications of Thermal Cameras
- Veterinary and Medical Use: They’re useful for detecting inflammation, infections, or circulation issues in animals and people, as thermal images can reveal abnormal temperature patterns.
- Building Inspection: Detecting heat leaks, electrical faults, moisture problems, and insulation issues in structures.
- Surveillance and Security: Night vision for security and military use, as they can detect people or animals hidden in the dark or behind obstructions.
- Search and Rescue: Finding people or animals in low-visibility conditions such as smoke, fog, or nighttime.
- Industrial Maintenance: Identifying overheated machinery or electrical equipment to prevent potential failures or accidents.
- Agriculture: Monitoring crop health, soil moisture, and even the body temperature of livestock.
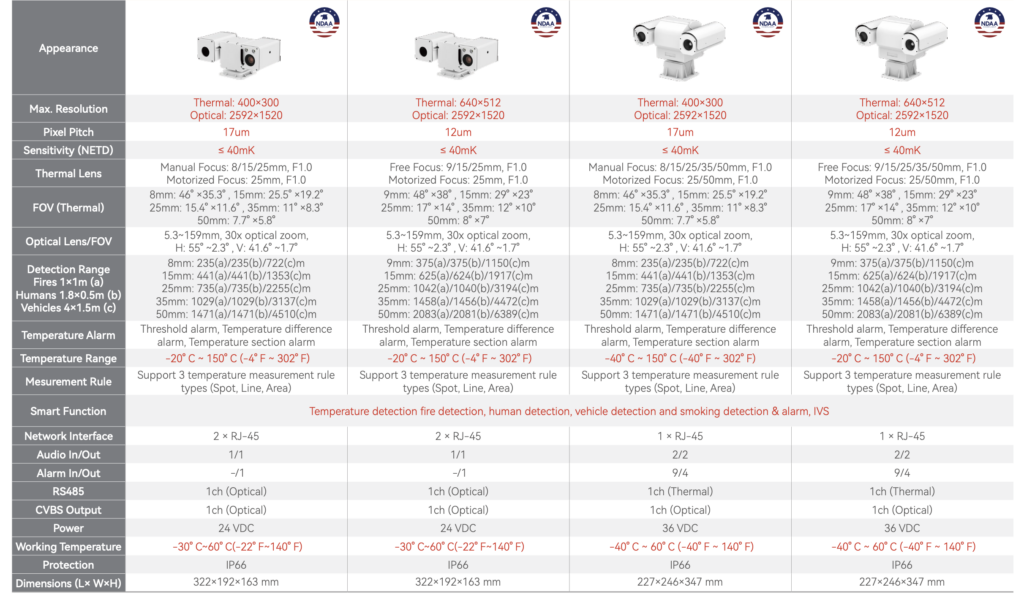
Bi-Spectrum Series
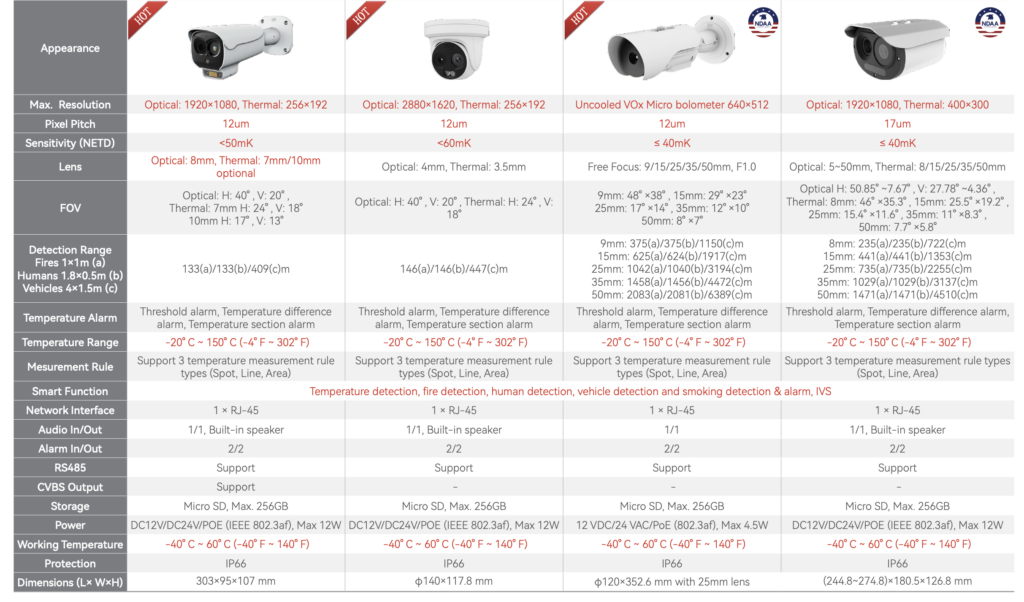
PTZ Thermal Series